The Role of Air Freight in the Netherlands’ Logistics Hub Status
The Netherlands stands as a beacon in global logistics, renowned for its exceptional connectivity and efficiency.
At the heart of this prowess is air freight, a cornerstone in the country’s supply chain management and trade facilitation. With a strategic location and world-class infrastructure, the Netherlands has become a preferred logistics gateway to Europe, offering unparalleled advantages to businesses across the globe.
From Amsterdam Schiphol Airport’s cutting-edge operations to the seamless integration of multimodal transport systems, the Netherlands has positioned itself as a leader in logistics. In this article, we’ll explore the critical role air freight plays in maintaining and enhancing the Netherlands’ status as a logistics hub.
Strategic Location and Connectivity
The Gateway to Europe
The Netherlands’ geographic location is one of its most significant assets. Nestled at the crossroads of Europe, it offers unmatched access to major markets. With over 170 million consumers reachable within 24 hours by road, the country is a linchpin for businesses seeking to penetrate the European market.
The integration of air freight with other transport modalities, including road, rail, and maritime routes, ensures smooth cargo transitions. The Port of Rotterdam, Europe’s largest seaport, complements Amsterdam Schiphol Airport, creating a robust logistics ecosystem that caters to diverse trade needs.
Amsterdam Schiphol Airport
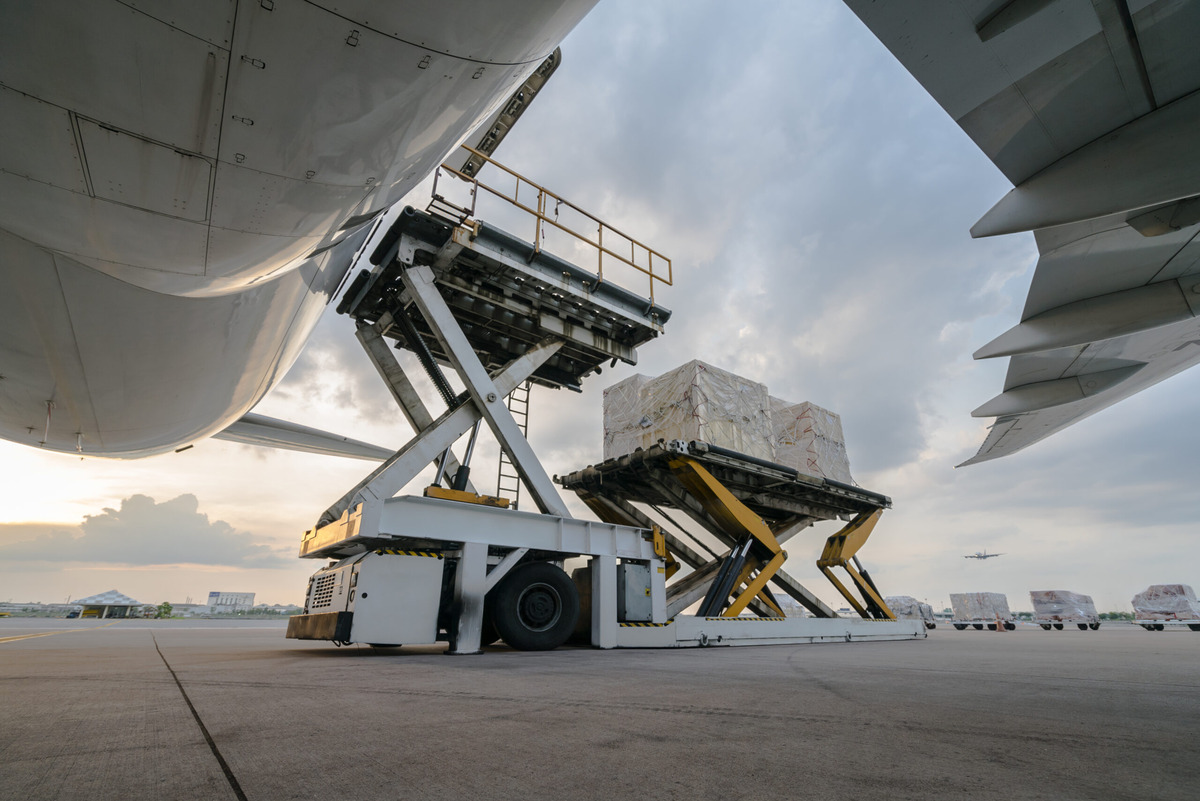
Amsterdam Schiphol Airport plays a pivotal role in positioning the Netherlands as a logistics powerhouse. Ranked among the world’s busiest airports, Schiphol boasts extensive global connectivity, linking the Netherlands to over 300 destinations. Its advanced cargo handling capabilities, including specialized facilities for temperature-sensitive goods, make it a preferred choice for industries like pharmaceuticals and fresh produce.
Moreover, Schiphol’s focus on innovation—such as real-time cargo tracking systems and efficient customs clearance processes—enhances its appeal to international logistics players. These factors collectively reinforce the airport’s role as a vital hub in global trade.
Advanced Infrastructure
State-of-the-Art Facilities
The Netherlands excels in providing cutting-edge infrastructure tailored for air freight logistics. Warehousing facilities near major airports are equipped with modern technologies to ensure optimal handling of goods. Dedicated cargo terminals and specialized storage solutions enable efficient management of a wide range of products, from perishables to high-value items.
Digital Innovations
Digital transformation has revolutionized air freight operations in the Netherlands. Technologies like automation, blockchain, and data analytics are streamlining supply chains, reducing costs, and enhancing transparency. For example, Schiphol’s Smart Cargo Hub initiative leverages artificial intelligence to optimize cargo flow, ensuring faster and more reliable deliveries.
Economic Contributions
Job Creation and Industry Growth
Air freight significantly boosts the Dutch economy, contributing billions to GDP and creating thousands of jobs. From logistics coordinators to cargo handlers, the sector supports a wide range of employment opportunities. The ripple effects extend to other industries, including manufacturing, retail, and agriculture.
Role in Supporting Other Sectors
Air freight’s ability to handle time-sensitive cargo underpins its importance to industries like e-commerce and pharmaceuticals. For instance, the transportation of COVID-19 vaccines relied heavily on the Netherlands’ efficient air freight network, demonstrating its critical role in global health and commerce.
Sustainability in Air Freight
Challenges in Environmental Impact
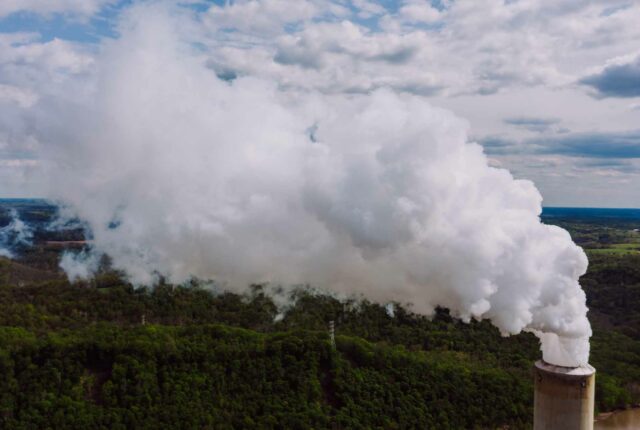
While air freight is indispensable for global trade, it is not without its challenges—particularly in terms of sustainability. Aircraft operations are significant contributors to carbon emissions, and the energy-intensive nature of air freight raises environmental concerns. Additionally, the reliance on fossil fuels and the high noise levels around airports pose challenges for both the industry and local communities.
Green Innovations in Air Freight
The Netherlands is actively addressing these issues through green initiatives. Amsterdam Schiphol Airport is a frontrunner in promoting sustainable practices, including the use of sustainable aviation fuel (SAF), which reduces carbon emissions by up to 80%. Electrification of ground handling equipment, investments in energy-efficient infrastructure, and initiatives to minimize cargo-related waste are further steps toward a greener future.
Collaborations with technology providers are also fostering the development of low-emission aircraft and the adoption of digital tools to optimize flight paths and reduce fuel consumption. These efforts position the Netherlands as a leader in sustainable air freight logistics.
Integration with Multimodal Logistics
One of the Netherlands’ standout features is its seamless multimodal logistics network. Air freight operations are strategically linked to road, rail, and sea transport, enabling efficient cargo transitions. For instance, goods arriving at Schiphol can be swiftly transported to Rotterdam for onward shipping or distributed across Europe via the country’s extensive highway and rail networks.
This level of integration not only enhances efficiency but also reduces overall transportation costs, making the Netherlands an attractive logistics hub for international businesses.
Challenges Facing the Industry
Regulatory and Capacity Issues
Despite its strengths, the air freight industry in the Netherlands faces several challenges. Regulatory constraints, including strict emissions targets and noise pollution limits, can impact operational flexibility. Additionally, capacity constraints at major airports, driven by increasing demand and limited expansion opportunities, pose significant hurdles.
The competition for airport slots among passenger and cargo flights adds to the complexity. As passenger air travel recovers post-pandemic, balancing the needs of both sectors will be crucial.
Global Trade Volatility
The air freight sector is particularly sensitive to global trade dynamics. Geopolitical tensions, economic slowdowns, and pandemics can disrupt supply chains and reduce cargo volumes. The Netherlands, as a major logistics hub, must navigate these uncertainties by diversifying its trade partnerships and investing in resilient infrastructure.
Air freight is a cornerstone of the Netherlands’ logistics ecosystem, driving economic growth, facilitating global trade, and connecting industries to international markets. The country’s strategic location, advanced infrastructure, and commitment to sustainability make it a standout logistics hub.
FAQs
What makes the Netherlands a leading logistics hub?
The Netherlands’ strategic location, world-class infrastructure, and seamless multimodal transport networks position it as a top logistics hub in Europe.
How does Amsterdam Schiphol Airport contribute to air freight logistics?
Schiphol Airport is a key hub with global connectivity, advanced cargo facilities, and innovative technologies that streamline logistics operations.
What are the challenges faced by the air freight industry in the Netherlands?
Major challenges include regulatory constraints, capacity limitations at airports, and global trade volatility.