The Role of Sea Freight in the Netherlands’ Trade-Driven Economy
The Netherlands is recognized as one of the most trade-dependent economies in the world. With a strong history in global commerce and an advantageous location in Europe, the country’s economic engine is powered by imports and exports across various sectors. Central to this thriving trade economy is sea freight, an essential link that connects Dutch ports with markets around the world. Thanks to its world-class port facilities and sophisticated logistics, the Netherlands serves as a vital gateway for Europe, facilitating the movement of goods efficiently and effectively.
Importance of Sea Freight in the Netherlands’ Economy
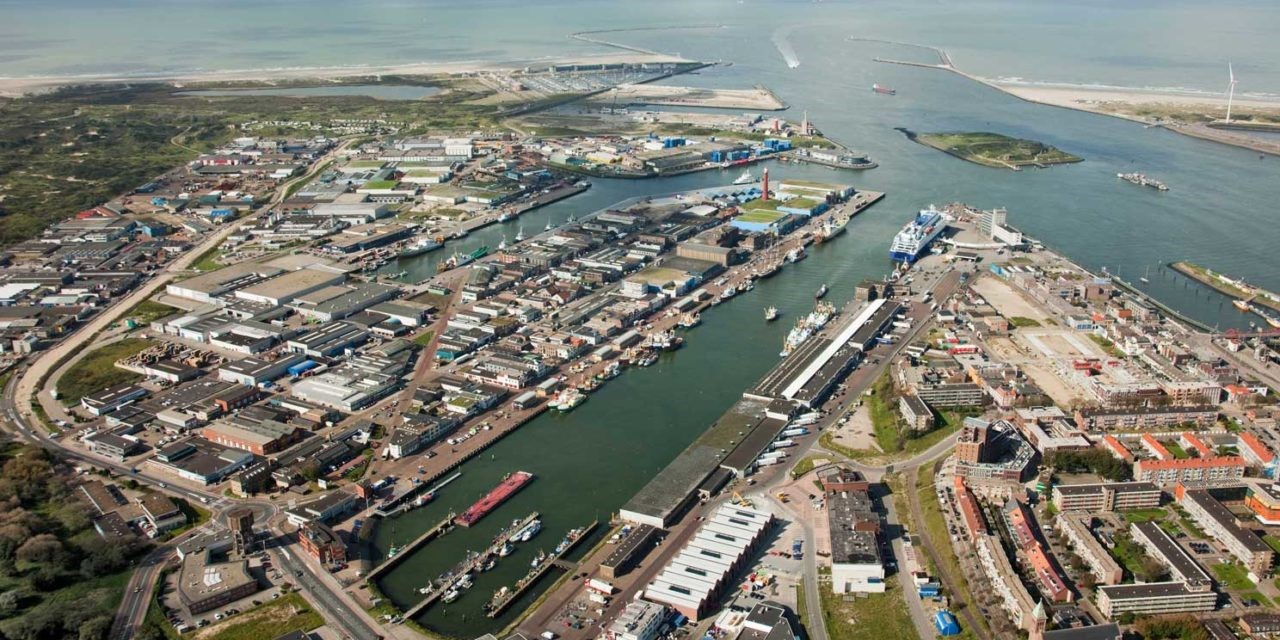
Sea freight forms the backbone of the Netherlands’ economy, moving millions of tons of goods each year and serving as a pillar for sectors like manufacturing, retail, and agriculture. Notably, the Port of Rotterdam—the largest port in Europe—acts as a crucial entry point for goods entering and leaving the continent. This strategic emphasis on sea freight has led to the development of a robust maritime infrastructure, contributing significantly to the country’s GDP and providing tens of thousands of jobs.
Historical Significance of Sea Freight in Dutch Trade
The Netherlands’ role in global sea trade dates back centuries. With its early adoption of maritime trade, the Dutch East India Company (VOC) rose to become one of the first multinational corporations, spearheading routes across Asia and Europe. This heritage of seafaring prowess shaped the Netherlands into a major trading power, a legacy that is visible in its modern ports and cutting-edge logistics practices.
Key Dutch Ports Driving Sea Freight
Port of Rotterdam as Europe’s Busiest Port
The Port of Rotterdam stands as the largest port in Europe and a critical logistical hub for goods entering and leaving the continent. Rotterdam handles a diverse array of goods, including energy commodities, consumer goods, food products, and chemicals, each day. This vast infrastructure enables Rotterdam to efficiently manage bulk cargo, container freight, and specialized shipments, making it a central node in the European supply chain.
Port of Amsterdam and Its Role in Trade
The Port of Amsterdam, while smaller than Rotterdam, is another pivotal port for the Netherlands. This port specializes in the trade of bulk goods and commodities, such as cocoa, coal, and oil. As a center for storage and transshipment, Amsterdam’s port complements Rotterdam’s role, facilitating access to the northern European markets.
Major Goods Transported via Sea Freight in the Netherlands
Agricultural Exports and Imports
The Netherlands is known for its agricultural prowess, especially in exports of flowers, dairy, fruits, and vegetables. The country’s extensive greenhouse farms and efficient production systems allow it to supply these goods worldwide, with sea freight playing a major role in the distribution of perishable goods. By leveraging cold-chain technology in shipping, Dutch sea freight maintains the freshness of food products during transport.
Energy Sector and Raw Material Imports
The Netherlands imports substantial volumes of crude oil, gas, and coal to fuel its industries and power its economy. Rotterdam’s role as an energy trade hub enables efficient import and distribution of these critical resources across Europe. Sea freight supports the Dutch energy sector by transporting large quantities of raw materials, contributing to energy security and industrial activity.
The Role of Sea Freight in the Netherlands’ Trade Relations
Trade with European Neighbors
With the European Union as a major trading bloc, the Netherlands uses sea freight to distribute goods across the continent. Products moving through Dutch ports reach customers throughout Europe, making the Netherlands a central player in intra-European trade. Efficient sea freight services strengthen the Netherlands’ economic integration with neighboring countries and bolster trade with the EU.
Global Trade Partnerships
Beyond Europe, the Netherlands maintains strong trade relationships with countries in Asia, the Americas, and Africa. Sea freight serves as the primary mode of transport in these international exchanges, with Dutch ports acting as key gateways for goods from around the world. Through streamlined logistics, the Netherlands reinforces its role as a global trade hub and supports the flow of goods to and from international markets.
Economic Challenges Facing Sea Freight in the Netherlands
Despite its strengths, Dutch sea freight faces economic challenges, including port congestion and fluctuating fuel prices. Increased shipping volumes can lead to delays and strain capacity, particularly in peak seasons. Additionally, higher fuel costs impact the profitability of sea freight, prompting Dutch companies to seek more sustainable, cost-effective shipping solutions.
Sea Freight’s Contribution to Employment and Local Economies
Sea freight not only drives national economic growth but also boosts local economies and employment. The industry supports thousands of jobs in logistics, port management, and maritime services. Moreover, businesses in surrounding regions benefit from the presence of bustling ports, which attract complementary industries such as warehousing, supply chain services, and hospitality.
Sea freight is indispensable to the Netherlands’ economy, forming a bridge that connects the country with the world. As Dutch ports continue to grow and innovate, the Netherlands stands poised to sustain its reputation as a leading trade hub. Embracing technology and sustainability, the Netherlands will likely remain a pivotal force in global logistics, enabling efficient and responsible trade for years to come.
FAQs
What role does sea freight play in the Netherlands’ economy?
Sea freight is a vital part of the Dutch economy, supporting trade, jobs, and key industries by enabling the movement of goods domestically and internationally.
How does the Port of Rotterdam contribute to Dutch trade?
The Port of Rotterdam is the largest in Europe, facilitating the import and export of diverse goods and making the Netherlands a central logistics hub.
What goods are commonly transported via Dutch sea freight?
Major goods include agricultural products, machinery, energy resources, consumer goods, and bulk commodities.